As part of the Health Resources Service Administration (HRSA) funded Maternal Health Innovations (MHI) Grant to reduce NC’s Maternal Mortality and Morbidity, the Provider Support Network is building partnerships and responding to identified needs of the providers in Perinatal Region IV. Through conversations with outpatient clinics, it came to our attention that many clinics do not have the resources or systems in place to quickly respond to patients with severe hypertension.
The national maternal safety bundles have primarily been focused on the inpatient setting. We have drafted an “Outpatient Severe Hypertension Bundle.” It consists of an adapted version of the AIM ACOG “Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy and Postpartum Bundle” (with the addition of a fifth “R” – “Respectful Care”).
We have adapted these materials in a Clinical Practice Bulletin for the outpatient setting, click here for the full practice bulletin.
Below you will find additional resources under each of the 5 R’s tab.
Take a look at the Alliance for Innovation on Maternal Health Inpatient Severe Hypertension Bundle
Review The California Maternal Quality Care Collaborative Comprehensive In-patient Toolkit
Every Outpatient Care Setting:
- Develop processes for management of pregnant and postpartum patients with severe hypertension, including:
- A standard protocol for maternal early warning signs, diagnostic criteria, monitoring and treatment of severe preeclampsia/eclampsia (including algorithms).
- A process for the timely triage and evaluation of pregnant and postpartum patients with severe hypertension or related symptoms who call or present to clinic.
- A plan for escalation, obtaining appropriate consultation, and maternal transfer as needed.
- Standards for educating prenatal and postpartum patients and support persons on early warning signs and how to get help, including printed materials.
- Ensure rapid access to medication used for treatment of severe hypertension.
- Conduct interprofessional and interdepartmental team-based drills with timely debriefs that include the use of simulated patients.
- Develop and maintain a set of referral resources and communication pathways between obstetric providers, community-based organizations, and state and public health agencies to enhance services and supports for pregnant and postpartum families.
- Develop trauma-informed protocols and provider education to address health care team member biases to enhance equitable care.
Readiness Resources:

ACOG Practice Bulletin 2020 Gestation and Hypertension
CMQCC Preeclampsia Early Recognition Tool
PMH Management of Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy
ACOG Hypertension Bundle (see slide 29)
Outpatient Severe Hypertension Evaluation and Management
CDC Hear Her Warning Signs Poster (Multiple Languages)
Every Patient:
- Ensure accurate measurement and assessment of blood pressure for every pregnant and postpartum patient, including via home blood pressure monitor if indicated.
- Screen for structural and social drivers of health that might impact clinical recommendations or treatment plans and provide linkage to resources that align with the pregnant or postpartum person’s health literacy, cultural needs, and language proficiency.
- Provide patient and support person education, including culturally appropriate resources and printed materials, on early warning signs of severe hypertension/pre-eclampsia and how to get help.
- Provide ongoing education to all health care team members on the recognition of signs, symptoms, and treatment of hypertension.
Recognition & Prevention Resources:
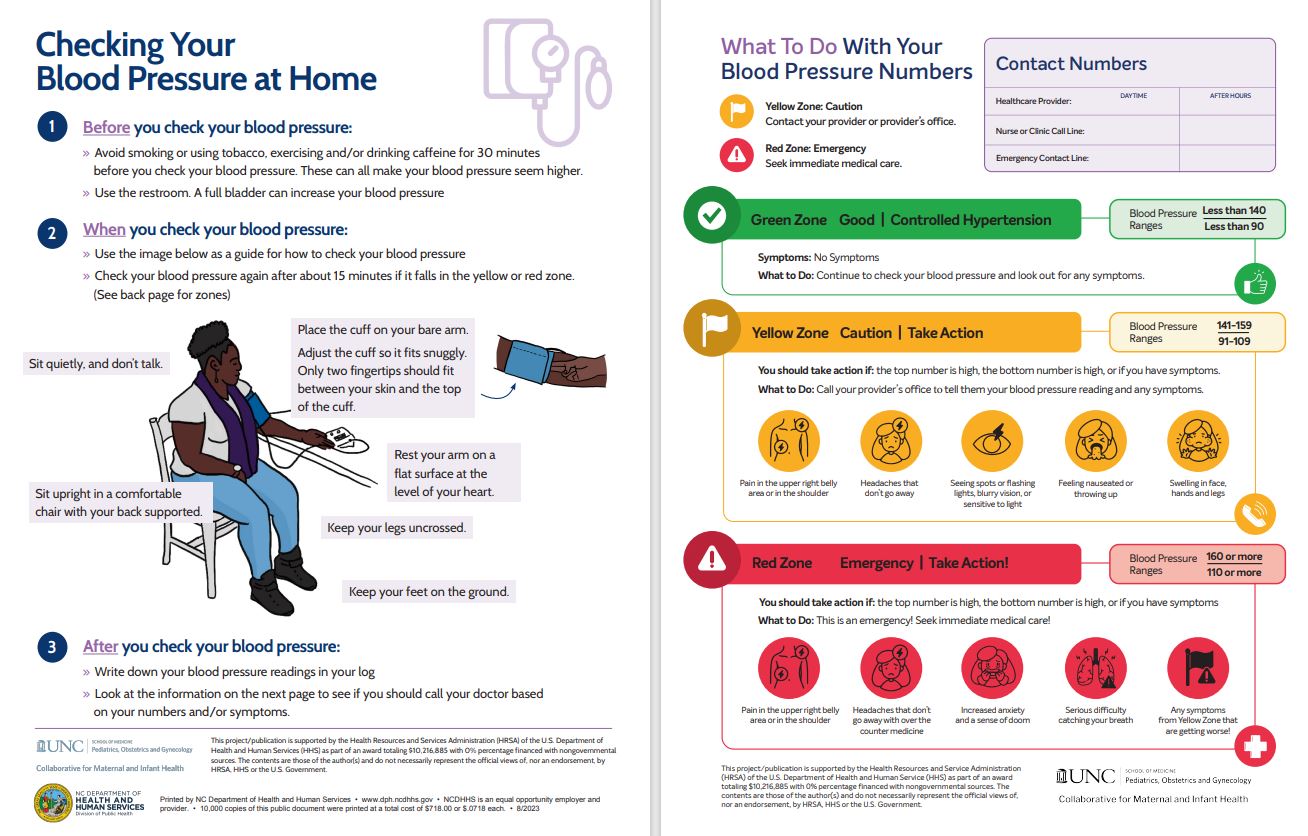
Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home and What to do with your Blood Pressure Numbers English, Spanish Version
CDC HEARHer for Partners, Friends and Family of Pregnant or Postpartum Women
Blood Pressure Log for Patients
The Maternal Early Warning Criteria
Every Case of Severe Hypertension:
- Utilize standardized protocols with checklists and escalation policies including:
- A standard response to maternal early warning signs
- Listening and investigation patient-reported and observed symptoms.
- Evaluation and management of episodes of severe hypertension/pre-eclampsia during pregnancy and postpartum
- Minimum Requirements for Protocol
- Notification of provider if systolic BP =/> 160 and/or diastolic BP =/> 110 (severe range) and retake in 15 minutes
- After the second severe range BP, treatment with oral Nifedipine IR (10 mg) should be initiated if available (ASAP, ideally within 30 minutes of BP verification)
- Escalation and care transition
- Maternal transport (algorithm) [Clinic Specific]
- Provide trauma-informed support for patients, identified support network, and staff for serious complications of severe hypertension, including discussions regarding birth events, follow up care, resources, and appointments.
Response Resources:
Outpatient Severe Hypertension Evaluation and Management
Treatment of Severe Range Blood Pressure Algorithm
ACOG Maternal Safety Bundle for Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy (See slide 29)
OB Hypertensive Emergency Nifedipine Task Checklist
ACOG Article: Postpartum preeclampsia or eclampsia: defining its place and management among the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
Case Study: Preeclampsia with Severe Features in the Outpatient Setting
Every Clinic:
- Establish a culture of multidisciplinary planning, huddles, and post-event debriefs for every case with severe hypertension/preeclampsia (include the patient and support person when feasible) to identify successes, opportunities for improvement, and action planning for future events.
- Perform multidisciplinary review of all severe hypertension/pre-eclampsia cases to identify systems issues.
- Monitor outcomes and process metrics related to severe hypertension disaggregated by race and ethnicity.
Reporting Systems/Learning Resources:
Outpatient Hypertension Debrief Form
Every Team Member/Every Clinic:
- Engage in open, transparent, and empathetic communication with pregnant and postpartum people and their identified support network to understand diagnoses, options, and treatment plans.
- Include pregnant and postpartum persons as part of the multidisciplinary care team to establish trust and ensure informed, shared decision-making that incorporates the pregnant and postpartum person’s values and goals.
- Ensure all educational resources and printed materials are appropriate for the patient’s health literacy, cultural needs, and language proficiency.
- Assess patient and support person’s understanding of the urgency of timely treatment of severe hypertension and escalation of care.
- Acknowledge patient’s concerns and assist with overcoming obstacles to going to the hospital (e.g., childcare, financial stress, past hospital-related trauma, etc.) and care plan (medication, appointments, antenatal testing).
- Implement strategies to mitigate racial/ethnic disparities identified through data collected.
Respectful, Equitable & Supportive Care Resources
Outpatient Hypertension Management Practice Bulletin can be downloaded and viewed here.
Hypertension Practice Bulletin Resources References:
- MSc JEM, Mph AVM, Pettker CM, Simhan AH. Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2020 Jun 6;135(6): e237–60.
- Paul G. Schmitz TN. Hypertension, Clinical Updates in Women’s Health Care. American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2016
- AIM PATIENT SAFETY BUNDLES [Internet]. ALLIANCE FOR INNOVATION ON MATERNAL HEALTH. 2021. Available from: https://saferbirth.org/psbs/severe-hypertension-in-pregnancy/
- Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System [Internet]. CDC Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternal-mortality/pregnancy-mortality-surveillance-system.htm
- Howell E et al. Reduction of Peripartum Racial and Ethnic Disparities: A Conceptual Framework and Maternal Safety Consensus Bundle. Journal of Midwifery & Women’s Health. 2019 May;63(3):353.
- HEAR HER Campaign [Internet]. CDC Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/hearher/index.html
- California Collaborative on District Reform. Available from: https://cacollaborative.org/
This project is supported by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) as part of an award totaling $10,216,885 with 0% percentage financed with non-governmental sources. The contents of those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of, nor an endorsement, by HRSA, HHS or the U.S. Government.” HRSA-funded. (C) 2020.
Please contact Liz Soto at lizso@email.unc.edu for more information